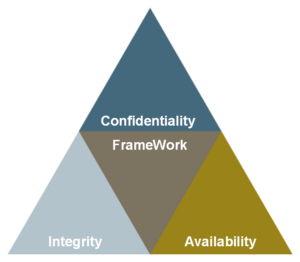
Enterprise Integrity Management defines all technical and operational facilities that are concerned with proving the integrity of important company data. Destruction and unwanted, often insidious, manipulation of sensitive data must be detected and prevented immediately. Organizations use EIM to protect their valuable digital infrastructure itself, or sensitive data stored on it by the company or its customers, from tampering. Proof of compliance with standards or legal regulations is also a component of EIM.
EIM refers to both protecting organizations from data tampering and its impact on ERP systems, production facilities, or the quality and security of manufactured goods. In this context, tampering also refers to targeted attacks on critical infrastructure, for example through a ransomware attack. Preventing data manipulation can also involve monitoring and securing configuration data and access authorizations.